COMPUTER SCIENCE
Unit no 10: Emerging technologies in Computer Science
Long Question Answers:
1. Discuss the various applications of AI in the field of education. Provide specific examples and explain how AI can enhance educational experience.
Uses of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is helping students and teachers in many new and smart ways. Here are some of the most common uses of AI in education, with easy examples:
- AI helps students learn at their own speed. If someone is slow in math, the computer can give easier questions and slowly increase the level.
Example: Khan Academy gives students lessons based on how well they are doing. - AI can act like a tutor that helps students when teachers are not around. It gives hints, explains mistakes, and helps solve problems.
Example: Some apps give step-by-step help in math, science, or English. - AI can check quizzes, multiple choice questions, and even short essays. This saves a lot of time for teachers.
Example: Online tests give results right away after you submit them. - AI can find out which subjects or topics a student is weak in and suggest more practice.
Example: If a student makes many mistakes in fractions, the AI suggests more practice questions on fractions. - AI tools can translate words or sentences into different languages. This helps students who don’t speak English well.
Example: Google Translate helps students understand homework in their own language. - Some schools use AI chatbots. Students can ask them questions like “When is the test?” or “What is homework for today?”
Example: A chatbot can reply to students at any time, even at night. - AI tools help students who can’t see or hear properly by reading out loud or showing captions.
Example: Microsoft Immersive Reader reads the text aloud for students with reading problems. - AI can mark attendance using face recognition and help teachers do routine work quickly.
Example: Face detection systems mark present or absent when students enter the classroom.
2. Differentiate between explainable (Whitebox) and unexplainable (Blackbox) AI models.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves using algorithms and techniques to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. In this section, we will explore different types of AI algorithms and understand their roles in advancing the capabilities of AI, particularly through machine learning models.
Types of AI Algorithms: Explainable (Whitebox) vs. Unexplainable (Blackbox)
AI algorithms can be broadly categorized into two types based on their interpretability: explainable (whitebox) and unexplainable (blackbox) algorithms.
Explainable (Whitebox) Algorithms
Explainable or whitebox algorithms are those where the decision-making process is transparent and understandable. These algorithms allow users to see and understand how decisions are made. Examples include:
Decision Trees: A decision tree is a tool that helps computers make decisions by following a series of questions. Each question leads to another question or a final answer, much like a flowchart.
Example: Let’s look at the example decision tree. This decision tree helps us identify an animal based on its characteristics.
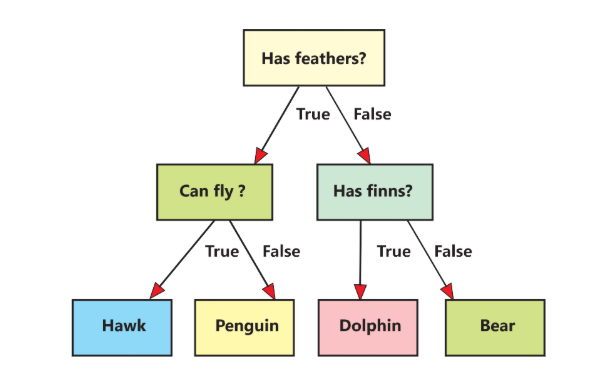
Linear Regression: Linear regression is a way to find the relationship between two features. Imagine you want to know how much time you should study to get good grades. Linear regression helps you find a straight line that best fits the data points showing study time and grades.
Example: If you have data showing how many hours you studied and the grades you got, linear regression can help you find a line that predicts your grade based on the number of hours you study. If the line shows that more study time generally leads to better grades, you can use this information to plan your study schedule.
Rule-Based Systems: Rule-based systems are like a set of “if-then” rules that computers follow to make decisions. These rules are written by humans to help the computer understand what to do in different situations.
Example: Think of a simple game where you control a character that needs to avoid obstacles. The game might use rules like “if the character is about to hit an obstacle, then jump.” These rules help the character move safely through the game.
Unexplainable (Blackbox) Algorithms:
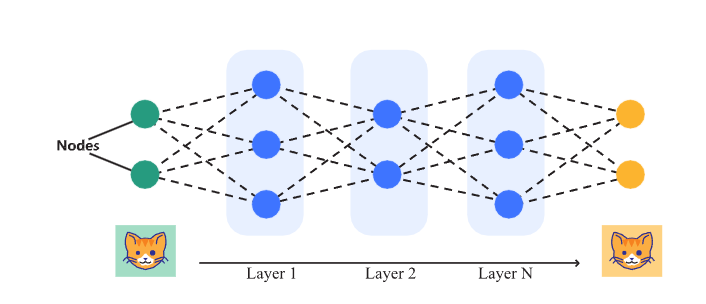
Unexplainable or blackbox algorithms are those where the decision-making process is not easily interpretable. These algorithms often involve complex computations and interactions that make it difficult to understand how a particular decision was reached. Examples include neural networks and deep learning models, which we have already discussed in previous Section.
3. Describe the components of an IoT system. Explain how these components work together to enable IoT applications.
IoT is a revolutionary concept that is transforming the way we live and work. It involves connecting everyday devices and systems to the internet, allowing them to communicate and interact with each other.
Definition:
IoT is a network of physical objects, or “things,” that are equipped with sensors, software, and other technologies to facilitate the exchange of data with other devices and systems over the internet. This facilitates the development of new, innovative services and the implementation of more intelligent, efficient operations.
Significance of IoT:
IoT is significant because it allows for the seamless integration of the physical and digital worlds. This connection enables devices to collect and share data, which can be analyzed to improve efficiency, provide better services, and create new opportunities in various fields such as healthcare, agriculture, and smart homes.
Components of IoT Systems:
An IoT system typically consists of the following components:
- Sensors: These are devices that detect and measure physical properties like temperature, humidity, light, and motion. Sensors collect data from the environment.
- Actuators: These are devices that convert energy into motion. In IoT, an actuator can act on data to generate output.
- Devices: These include everyday objects like smartwatches, refrigerators, and cars that are connected to the internet. Devices use the data collected by sensors to perform specific tasks.
- Networks: These are the communication pathways that connect sensors and devices to the internet, allowing them to share data. Networks can be wired or wireless.
- Data Analysis: This involves processing and analysing the data collected by sensors to gain insights and make decisions. Data analysis can be done on the device itself, in the cloud, or on a central server.
4. Explore the applications of IoT in the transportation domain.
IoT is enhancing transportation systems, making them more efficient and safer. Connected vehicles, smart traffic lights, and real-time tracking systems are some examples of how IoT is used in transportation.
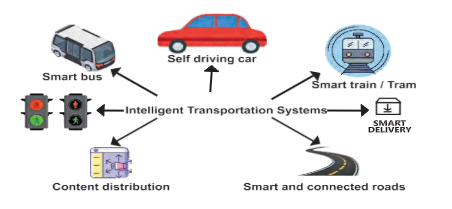
The IoT is changing the transportation industry through a variety of applications that improve efficiency and safety. Smart traffic management systems use IoT sensors to monitor traffic flow in real time, altering traffic lights to reduce congestion. In fleet management systems, IoT sensors track cars in real time, providing data on position, speed, and maintenance requirements to help routes and fuel use.
5. Analyze the potential privacy concerns associated with IoT deployments. Or What are the implications and challenges of AI and IoT?
Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things are rapidly transforming various aspects of our lives. While these technologies offer numerous benefits, they also present several implications that need to be carefully considered.
Implications of AI and IoT
- Risks and Challenges
Potential Risks Associated with AI and IoT:
Data Privacy: As AI and IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, concerns about data privacy become paramount. Personal and sensitive information can be at risk of being misused or accessed by unauthorized parties. Ensuring data privacy involves implementing robust security measures to protect data from breaches and unauthorized access.
Algorithmic Bias: Training of AI systems is conducted on large datasets, and if these datasets comprise biases, the AI models can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify these biases. This can lead to unfair outcomes in various applications, such as hiring processes, law enforcement, and lending practices. Addressing algorithmic bias makes analysis of training data and implementing techniques to relieve biases.
6. Evaluate the impact of AI and IoT on the job market and work environments.
Job Market:
AI and IoT are altering the job market by introducing new roles in sectors such as AI development and IoT management, while also removing typical, manual jobs in industries like manufacturing. This change underscores the importance of reskilling, as demand for technical and analytical abilities rises.
Work Environments:
AI is revolutionizing workplaces by automating repetitive tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling data-driven decision-making. IoT devices in industrial settings optimize production processes and monitor equipment health, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
7. Explain the role of policy and regulatory frameworks in addressing the challenges of AI and IoT. Provide examples of existing frameworks and discuss their effectiveness.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks Addressing AI and IoT Challenges:
To mitigate the risks associated with AI and IoT, comprehensive policy and regulatory frameworks are essential. These frameworks should focus on:
- Data Protection Laws: Implementing strict data protection regulations to ensure that personal data is collected, stored, and processed securely. Examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
- Ethical Guidelines: Establishing ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability. Organizations like the IEEE have developed guidelines for ethical AI.
- Bias Mitigation Standards: Developing standards and best practices for identifying and mitigating biases in AI models. This includes guidelines for diverse and representative data collection and techniques for bias detection and connection.
- Security Standards: Enforcing security standards for IoT devices to protect them from cyber-attacks. This includes regular software updates, encryption, and secure authentication mechanisms.
8. Describe the concept of algorithmic bias and its implications in AI-powered decision-making processes. Suggest strategies to mitigate the risks of algorithmic bias.
Algorithmic Bias:
Training of AI systems is conducted on large datasets, and if these datasets comprise biases, the AI models can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify these biases. This can lead to unfair outcomes in various applications, such as hiring processes, law enforcement, and lending practices. Addressing algorithmic bias makes analysis of training data and implementing techniques to relieve biases.
Algorithmic bias happens when an AI system makes unfair decisions because it learns from data that contains hidden prejudices. For example, if an AI is trained on job applications that mostly come from one group of people, it might learn to prefer that group and ignore others. This can lead to unfair results, like not giving someone a loan, job, or fair chance just because of their background, race, or gender. It’s a serious problem because people start losing trust in technology, and it can even break laws meant to protect against discrimination.
To stop this, we need to train AI using data that includes people from all walks of life. Developers should also regularly test their AI systems to make sure they treat everyone fairly. Making AI decisions easier to understand and keeping humans involved in important choices can also help. Most importantly, people from different backgrounds should be part of the teams that design and test AI, so the system works well for everyone.
9. Develop a set of ethical principles and guidelines for the responsible development and deployment of AI and IoT technologies.
To ensure the responsible development and use of AI and IoT technologies, it is important to follow a set of ethical principles. First, these technologies should be fair and treat everyone equally, without showing bias based on race, gender, or background.
Privacy must also be protected, meaning personal data like photos, voice recordings, or location should be kept safe and not shared without permission. AI and IoT systems should be transparent, so people can understand how they work and why certain decisions are made. It’s also important that there is accountability—someone must take responsibility if something goes wrong.
Humans should always stay in control, especially when it comes to serious matters like health or safety. These systems must be reliable and tested properly to avoid harm. Developers should also think about the environment and design technology that uses energy efficiently. Lastly, AI and IoT should be accessible and inclusive, so people of all abilities and backgrounds can benefit from them. By following these guidelines, we can make sure that technology helps everyone in a fair and safe way.
