Study Guide
A Comprehensive Overview of Systems and Computer Architecture
Natural & Artificial Systems
Q.1 Define Natural System.
Natural systems are those that exist in nature and operate independently of human involvement. They are governed by natural laws and process.
Q.2 Mention some examples of Natural System.
- Physical systems
- Chemical systems
- Biological systems
- Psychological systems
Q.3 Differentiate between Physical and Chemical Systems.
Physical systems are composed of physical components and governed by the laws of physics. They include things ranging from sub-atomic particles, atoms, planets, stars, and galaxies. Chemical systems involve substances and their interactions, transformations, and reactions. They are governed by the laws of chemistry.
Q.6 What are the Artificial Systems?
Artificial systems are created and developed by people so that they may fulfill certain functions or address certain issues. These systems can be as small as a wheel or as large as the United Nations.
Q.17 How would you relate System with Science?
Knowledge is our understanding of various systems in the universe around and within us. Science is a systematic way to validate this understanding. Science can be divided into two main types: natural science and design science.
Q.18 Draw the diagram of empirical cycle.
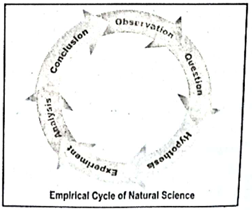
Q.19 What is Design Science?
Design Science is focused on designing and creating artifacts (tools, systems, methods) to achieve specific goals. The nature of design science is prescriptive, meaning that it aims to prescribe and create artificial systems.
Q.20 Draw the diagram of Regulative Cycle.
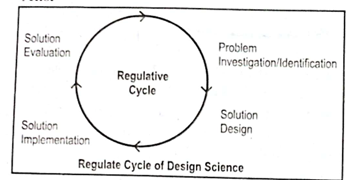
Von Neumann Architecture & Internet Protocols
Q.22 What is the main objective of a computer?
The main objective of a computer is to perform computations, process data, and execute different tasks efficiently. For example, a personal computer’s objective is to run software applications such as word processors, web browsers and games.
Q.28 Differentiate between Hardware and Software.
Hardware of a computer system refers to the tangible components of the system. These include the Central Processing Unit (CPU), Random Access Memory (RAM), storage devices, and input and output devices. Software refers to a collection of instructions that dictate the requirements and actions that hardware must do. The two primary categories are: System software and application software.
Q.24 Draw Von Neumann Architecture.
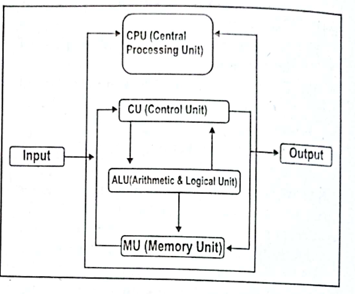
Q.25 What are the components of Von Neumann Architecture?
- Memory
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Input devices
- Output devices
Q.27 Make list of working components of Von Neumann Architecture.
- Fetching
- Decoding
- Execution
- Storing
Q.26 What are the main types of Buses?
- Data Bus: Transports data.
- Address Bus: Maintains data destination information.
- Control Bus: Transports and control electrical signals.
Q.29 What are the Internet Protocols?
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The core protocols that govern data transmission over the internet.
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP): Faster but less reliable.
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Used for transferring files between computers.
- Post Office Protocol (POP): Used for retrieving emails from a server/network.
