Unit no 07: Computational Thinking
Long Question Answers:
- Write an algorithm to assign a grade based on the marks obtained by a student. The grading system follows these criteria:
- 90 and above: A+
- 80 to 89: A
- 70 to 79: B
- 60 to 69: C
- Below 60: F
Start
Input: Marks obtained by the student (let’s call it marks)
If marks >= 90, assign grade as A+
Else if 80 <= marks < 90, assign grade as A
Else if 70 <= marks < 80, assign grade as B
Else if 60 <= marks < 70, assign grade as C
Else, assign grade as F
Output: Display the assigned grade
End
- Explain how you would use algorithm design methods, such as flowcharts and pseudocode, to solve a complex computational problem. Illustrate your explanation with a detailed example.
Algorithm design methods provide a range of tools and techniques to tackle various computational problems effectively. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different types of problems. Understanding different methods allows one to choose the most appropriate approach for a given problem, leading to more efficient and elegant solutions. Let’s discuss two of these methods.
Flowcharts
Flowcharts are visual representations of the steps in a process or system, depicted using different symbols connected by arrows. They are widely used in various fields, including computer science, engineering, and business, to model processes, design systems, and communicate complex workflows clearly and effectively.
Importance of Flowcharts
- Clarity: Flowcharts provide a clear and concise way to represent processes, making them easier to understand at a glance.
- Communication: They are excellent tools for communicating complex
processes to a wide audience, ensuring everyone has a common understanding.
- Problem Solving: Flowcharts help identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in a process, aiding in problem-solving and optimization.
- Documentation: They serve as essential documentation for systems and processes, which is useful for training and reference purposes.
Flowchart Symbols
Flowchart symbols are visual representations used to illustrate the steps and flow of a process or system.

- Define computational thinking and explain its significance in modern problem-solving. Provide examples to illustrate how computational thinking can be applied in different fields.
Computational Thinking (CT) is a problem-solving process that involves a set of skills and techniques to solve complex problems in a way that a can be executed by a computer. This approach can be used in various fields beyond computer science, such as biology, mathematics, and even daily life.
Let’s break down computational thinking into its key components:
Decomposition:
Decomposition is the method of breaking down a complicated problem into smaller, more convenient components. Decomposition is an important step in computational thinking. It involves dividing a complex problem into smaller, manageable tasks. Let’s take the example of building a birdhouse. This task might look tough at first, but if we break it down, we can handle each part one at a time.
Here’s how we can decompose the task of building a birdhouse. Figure 7.1 shows the decomposed tasks for building a birdhouse.
- Design the Birdhouse: Decide on the size, shape, and design. Sketch a plan and gather all necessary measurements.
- Gather Materials: List all the materials needed such as wood, nails, paint, and tools like a hammer and saw.
- Cut the Wood: Measure and cut the wood into the required pieces according to the design.
- Assemble the Pieces: Follow the plan to assemble the pieces of wood
together to form the structure of the birdhouse.
- Paint and Decorate: Paint the birdhouse and add any decorations to make it attractive for birds.
- Install the Birdhouse: Find a suitable location and securely install the
birdhouse where birds can easily access it.
- Discuss the concept of decomposition in computational thinking. Why is it important?
Decomposition is a key notion in computational thinking that entails dividing a large problem or system into smaller more manageable components. This technique simplifies the problem making it easier to comprehend, evaluate and resolve. Decomposition, by focusing on individual components aids in the identification of patterns streamlines the problem-solving process and ensures clarity. It is especially significant in software development where huge projects can be broken down into modules such as user interface design backend development and database management. This modular approach not only improves knowledge but it also increases efficiency because different components can be worked on concurrently by different teams or people. Furthermore, deconstruction makes solutions to smaller sub problems more reusable as they can often be applied to other projects or settings it also promotes scale ability by allowing systems to evolve or adapt through changes to individual components rather than redesigning the entire system over all decomposition is an effective technique for structured problem-solving modularity and efficiency in computational thinking and beyond.
- Explain pattern recognition in the context of computational thinking. How does identifying patterns help in problem-solving?
Pattern recognition involves looking for similarities or patterns among and within problems. For instance, if you notice that you always forget your homework on Mondays, you might recognize a pattern and set a reminder specifically for Sundays.
Pattern recognition is an essential aspect of computational thinking. It involves identifying and understanding regularities or patterns within a set of data or problems. Let’s consider the example of recognizing patterns in the areas of squares.
The upper row in Figure 7.2 represents the side lengths of squares, ranging from 1 to 7. The lower row shows the corresponding areas of these squares. Here, we can observe a pattern in how the areas increase.
- Side Length 1: Area = 12 = 1
- Side Length 2: Area = 22 = 4 (1 + 3)
- Side Length 3: Area = 32 = 9 (1 + 3 + 5)
- Side Length 4: Area = 42= 16 (1 + 3+ 5 + 7)
- Side Length 5: Area = 52= 25 (1 + 3 + 5+ 7 + 9)
- Side Length 6: Area = 62= 36 (1 + 3 + 5+ 7 + 9 + 11)
- Side Length 7: Area = 72= 49 (1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11+ 13)
We can see that the area of each square can be calculated by adding consecutive odd numbers. For example, the area of a square with a side length of 3 can be found by adding the first three odd numbers: 1 + 3 + 5 = 9.
Visual/Numerical Pattern
Goes up by 1
Goes up by consecutive odd numbers starting at 3
- What is an abstraction in computational thinking? Discuss its importance and provide examples of how abstraction can be used to simplify complex problems.
Abstraction is a fundamental concept in problem solving, especially in computer science. It involves simplifying complex problems by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable parts, and focusing only on the essential details while ignoring the unnecessary ones. This helps in understanding, designing, and solving problems more efficiently.
- Definition: Abstraction is the process of hiding the complex details while exposing only the necessary parts. It helps reduce complexity by allowing us to focus on the high-level overview without getting lost in the details.
- Example:
Making a Cup of Tea – High-level Steps:
1. Boil water.
2. Add tea leaves or a tea bag.
3. Steep for a few minutes.
4. Pour into a cup and add milk/sugar if desired.
- Describe what an algorithm is and explain its role in computational thinking. Provide a detailed example of an algorithm for solving a specific problem and draw the corresponding flowchart.
An algorithm is a step- by- step collection of instructions to solve a problem or complete a task similar to following a recipe to bake a cake..
An algorithm is a precise sequence of instructions that can be followed to achieve a specific goal, like a recipe or a set of directions that tells you exactly what to do and in what order.
- Example: Planting a Tree: Here is a simple algorithm to plant a tree, an activity that can be very meaningful and beneficial:
- Choose a suitable spot in your garden.
- Dig a hole that is twice the width of the tree’s root ball.
- Place the tree in the hole, making sure it is upright.
- Fill the hole with soil, pressing it down gently to remove air pockets.
- Water the tree generously to help it settle.
- Add mulch around the base of the tree to retain moisture.
- Water the tree regularly until it is established.
This algorithm gives clear instructions on how to plant a tree, making it easy to follow for anyone.
- Compare and contrast flowcharts and pseudocode as methods for algorithm design. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method and provide examples where one might be preferred over the other.
Flowcharts and pseudocode are both tools used to describe algorithms, but they do so in different ways. Understanding their differences can help you decide which method is more suitable to use for your scenario.
| Pseudocode | Flowcharts |
| Pseudocode uses plain language and structured format to describe the steps of an algorithm.It is read like a story, with each step is written out sequentially.Pseudocode communicates the steps in a detailed, narrative -like format.It is particularly useful for documenting algorithms in a way that can be easily converted into actual code in any programming language. | Flowcharts use graphical symbols and arrows to represent the flow of an algorithm.It is like watching a movie, where each symbol (such as rectangles, diamonds, and ovals) represents a different type of action or decision, and arrows indicate theconnection and direction of the flow.Flowchart communicates the process in a visual format, which can be more intuitive for understanding the overall flow and structure.They are useful for identifying the steps and decisions in an algorithm at a glance. |
Example:
Algorithm: Presents the pseudocode for checking a valid username and password.
- Procedure Check Credentials (username, password)
- Input: username, password
- Output: Validity message
- Begin
- validUsername = “user123” {Replace with the actual valid username}
- validPassword = “pass123” {Replace with the actual valid password}
- if (username == validUsername) then
8: if (password == validPassword) then
9: print “Login successful”
10: else
11: print “Invalid password”
12: end if
13: else
14: print “Invalid username”
15: end if
16: End
- Explain the concept of a dry run in the context of both flowcharts and pseudocode. How does performing a dry run help in validating the correctness of an algorithm?
A dry run involves manually going through the algorithm with sample data to identify any errors.
Dry Run of a Flowchart
A dry run of a flowchart involves manually walking through the flowchart step-by-step to understand how the algorithm works without using a computer. This helps identify any logical errors and understand the flow of control.
Example: Calculating the Sum of Two Numbers
Consider the flowchart given in figure 7.7 for adding two numbers:
Steps to dry run this flowchart:
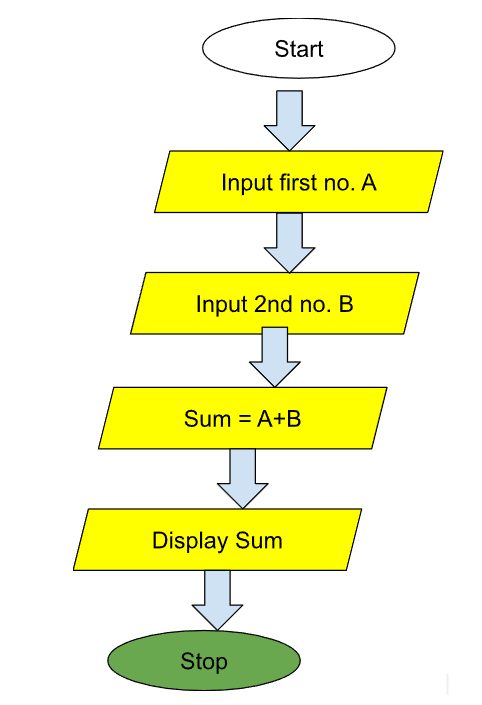
- Start
- Input the first number (e.g., 3)
- Input the second number (e.g., 5)
- Add the two numbers (3 + 5 = 8)
- Output the result (8)
- Stop
Dry Run of Pseudocode
A dry run of pseudocode involves manually simulating the execution of the pseudocode line-by-line.
This helps in verifying the logic and correctness of the algorithm. Example: Finding the Maximum of Two Numbers Consider the pseudocode for finding the maximum of two numbers:
Algorithm 4 FindMax
- Input: num1, num2
- if num1 > num2 then
- max = num1
- else
- max = num2
- end if
- Output: max
Steps to dry run this pseudocode:
- Input num1 and num2 (e.g., 10 and 15)
- Check if num1 > num2 (10>15: False)
- Since the condition is False, max = num2 (max = 15)
- Output max (15)
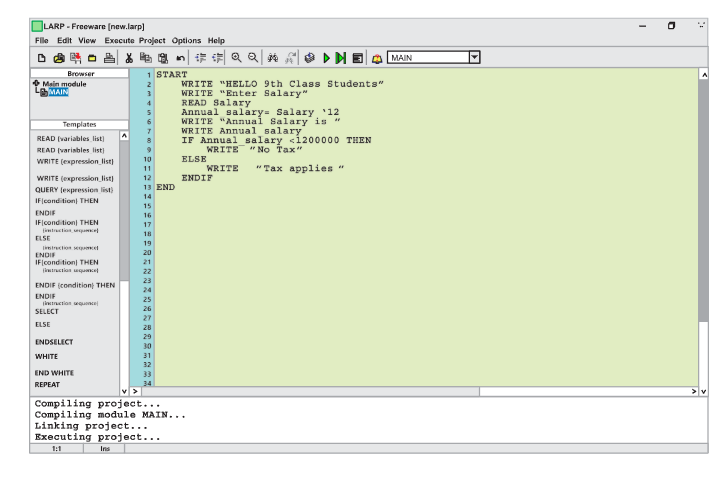
- What is LARP? Discuss its importance in learning and practicing algorithms.
LARP stands for Logic of Algorithms for resolution of Problems. It is a fun and interactive way to learn how algorithms work by actually running them and seeing the results. Think of it as a playground where you can experiment with different algorithms and understand how they process data.
Why is LARP Important?
LARP helps you:
- Understand how algorithms work. For instance, refer to Figure 7.9, which illustrates an algorithm designed to determine the applicability of tax on the annual salary of a person.
- See the effect of different inputs on the output.
- Practice writing and improving your own algorithms.
Writing Algorithms
Writing algorithms using LARP involves a structured and simplified approach to developing logical solutions for computational problems. LARP employs a clear syntax that begins with a START command and ends with an END command, ensuring that each step of the algorithm is easy to follow. Within this framework, instructions are provided in a straightforward manner, such as using WRITE to display messages, READ to input values, and conditional statements like IF…THEN…ELSE to handle decision-making processes. By breaking down complex problems into manageable steps, LARP allows learners to focus on the logical flow of the algorithm without getting stuck on complex coding syntax. This method not only aids in understanding the fundamental concepts of algorithm design but also enhances problem-solving skills by encouraging clear and logical thinking.
Here’s an example of a simple algorithm to check if a number is even or odd:
START
WRITE “Enter a number” READ number IF number % 2 == 0 THEN
WRITE “The number is even”
ELSE
WRITE “The number is odd”
ENDIF END
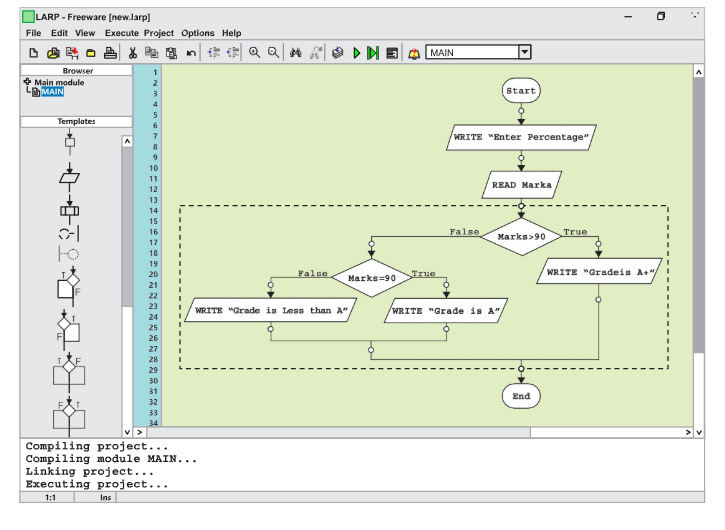
Drawing Flowcharts in LARP
Drawing flowcharts in LARP involves visually representing the algorithm’s steps using standard flowchart symbols such as rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions, and parallelograms for input/output operations.
- How does LARP enhance the understanding and application of computational thinking principles? Provide a scenario where LARP can be used to improve an algorithm.
LARP improves the knowledge and implementation of computational thinking principles by taking an immersive, interactive, and collaborative approach to problem solving. Participants gain hands-on experience decomposing complicated issues, identifying patterns, abstracting pertinent information, and designing successful algorithms through role-playing situations that replicate real-world challenges. LARP makes abstract topics tangible by requiring participants to actively create and test solutions while receiving quick feedback, which encourages incremental improvements. This strategy focuses on collaboration and adaptation, reflecting the dynamic nature of computational problem solving.
Consider a case in which LARP is used to develop a sorting algorithm for organizing volumes in a library based on height. Participants assume roles such as “librarian”, “books”, and “observers”.
The librarian employs an initial algorithm, such as bubble sort, to arrange participants (books) according to their displayed height.
